HEARING LOSS EXPLAINED
EVERYTHING YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT HEARING PROBLEMS
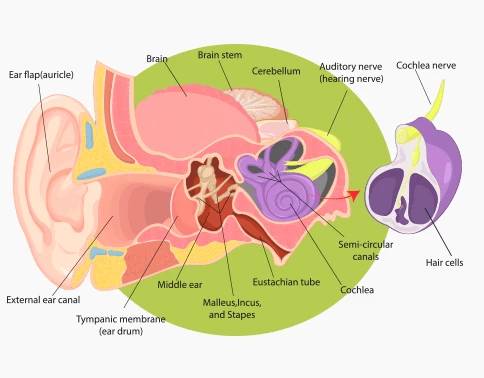
How We Hear:
Hearing Basics
Hearing loss is considered to be one of the most important healthcare issues. Unfortunately, nearly 170 million people worldwide are affected by this disease. When talking about hearing impairment, we mean an absolute or partial inability to hear sounds. The problems with ears tend to occur right after birth. In fact, hearing loss affects nearly 4 out of every 1000 newborns. However, the disease can develop and get worse at any age. Thus, we want to make our clients aware of hearing impairment and its prevention.
As far as ear anatomy is concerned, this sensitive organ consists of the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The primary function of the outer part is to collect and send sounds to the ear canal. Then the eardrum, in the middle ear, produces vibrations that are transferred through small bones to the inner ear. The inner ear houses the cochlea, which has many tiny hair-like cells that respond to sound. Finally, these cells send the nerve signals to the brain. That is how a sound is born.
Types and symptoms
of hearing impairment

- SENSORINEURAL Hearing Loss is the most common type of hearing loss. Damage occurs to the inner ear and/or auditory nerve. Causes: Age-related changes in the body, exposure to loud noises, medications, or genetic disposition. Treatments: Hearing aids are very successful at correcting this type of hearing loss.
- MIXED Hearing Loss is a combination of Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Conductive Hearing Loss. Causes: Aging, head injuries, ear malformation, genetic factors. Treatments: The nature of the loss will determine the treatment.
- CONDUCTIVE Hearing Loss occurs when sounds entering the outer ear are not transmitted correctly to the inner ear. Causes: Perforated eardrum, fluid in the middle ear, or infectious lesions in the outer and/or middle ear. Treatments: Medical treatment or surgery is usually necessary.
- TINNITUS is an ear disorder common among adults. It is most commonly described as a ringing sound in the ears, but it can also manifest as a whistling, roaring, hissing, or buzzing sound. People with severe tinnitus face huge problems in everyday life: inability to sleep, lack of focus at work, or reduced ability to handle psychological stress. Causes: Wide variety of reasons, including exposure to loud noises, ear infections, and certain medications. Treatments: When used consistently, hearing aids provide tinnitus relief, with the added benefit of hearing correction.
the human brain
hearing loss
A study made by Johns Hopkins Medicine, a leading health care center worldwide, revealed that there is a strong connection between hearing impairment and brain function. Hearing loss is shown to contribute to brain atrophy. As a result, people with untreated hearing dysfunctions are likely to face decreased cognition, which can lead to dementia.
In fact, a group of professional audiologists compared the brain structures of people with normal hearing to those of people with impaired hearing. They concluded that people with hearing loss had certain brain structures that had become smaller. This process leads to further shrinkage in the areas of the brain responsible for sound, speech, memory, and comprehension.
Dr. Frank Lin, the primary researcher, highlights the need for urgent treatment of hearing impairments. In order to prevent dangerous and potentially fatal changes in brain structures, it is better to address such health problems without delay. You can get a real benefit from hearing aids that help your brain better process sounds and properly interpret them.

Consequences of untreated
Hearing Loss

WHAT YOU CAN EXPECT FROM UNTREATED HEARING LOSS:
- Physical Effects: The brain starts over-processing, trying to put together signals that it is no longer receiving. As a result, there may be fatigue (lack of energy), disorientation (frequent falls), prolonged periods of illness, depression/stress, headaches, hypertension, insomnia, and/or tinnitus.
- Cognitive Effects: Dysfunction of hearing causes brain atrophy. People often experience difficulty in processing speech or filtering speech from background noise. As a result, there is a loss of brain tissue that can lead to dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
- Social Effects: Hearing loss has a detrimental impact on personal fulfillment. Hearing loss results in fear, incompetence, anger, stress, paranoia, and even isolation from family. Additionally, hearing impairment is connected with the loss of one’s independence and earning potential.
Want to Learn More About Hearing?
Contact us and our experts would be happy to provide a
comprehensive consultation on hearing and hearing loss.